Introduction to 8051 Microcontroller
A microcontroller is nothing but a small computer on a single integrated circuit , it consist of central processing unit, memory unit, and programmable input/output peripherals. Memory unit consist of ROM as well as RAM. Microcontrollers are generally designed for embedded applications that is dedicated applications which different than the microprocessors which are used in personal computers or general purpose applications.
Intel made 8051, referred as MCS- 51, in 1981.The 8051 is an 8-bit processor, its mean that CPU can work on only 8 bits of data at a time.The 8051 became widely popular when Intel allowed other manufactures in the market to make any flavor of the 8051.
MCS- 51 Family:
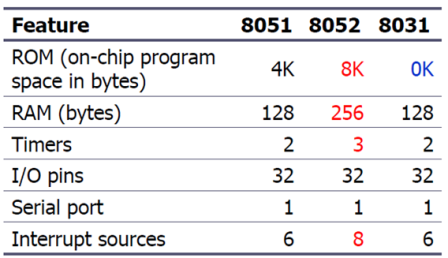
The 8051 is a father of MCS-51 family because it is the original member of 8051 family.The 8052 is a subset of the 8051 The 8031 is a ROM-less 8051Add external ROM to it.You lose two ports, and leave only 2 ports for I/O operations.
Features of 8051 : Following are the features of 8051.
- 64KB Program Memory address space
- 64KB Data Memory address space
- 4KB on-chip Program Memory
- 128 bytes of on-chip Data RAM
- 32 I/O lines
- 4 register banks of 8 bytes each (R0 to R7)
- Two 16-bit timer/counters
- on-chip Full duplex UART
- 5 vector interrupt sources ( 2 external, 3 internal )
- On-chip clock oscillator
As seen in features, the 8051 microcontroller has nothing impressive appearance: 4 Kb of ROM is may be not much at all in some application. 128b of RAM which includes SFRs also not great . 4 ports with total 32 input/output lines But,the whole configuration can fulfill the needs of most programmers working on development of automation devices .One of its mostly noted advantages is that nothing is missing and nothing is too much. In short, it can fulfill average user‘s requirement.
8051 Block Diagram:
8051 block diagram consist of following parts:
CPU: Central processing unit (CPU) is a brain of processor. The main components of a CPU are the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which is used to perform arithmetic and logical operations, and the control unit (CU), which is used to extracts instructions from memory,decode it and executes them, also calls the ALU as per necessity.
We are mostly familiar with Central Processor Unit or CPU of computer. It manages as well as scrutinizes all processes that are carried out in the Computer. CPU executes the program written in (ROM) and do the projected duty.
Memory: Micro-controller i.e CPU needs the program's to do a specific tasks which is a set of commands. We have to store these programs on storage space i.e. memory . The memory which is used to store the program of Microcontroller is called as Program memory or generally we call it as a code memory. In most common language we call it "Read Only Memory" or ROM. Micro-controller also needs a short term memory space to perform operation on data stored in ROM . The storage space which is used for temporary data storage is called as Random Access Memory or RAM . 8051consist of program memory 4K byte and 128 bytes of a data RAM .
Bus: Bus is nothing but group of connecting wires which are used for the transfer Data. These buses are consist of 8, 16 or even more than that wires generally . Hence, a bus can carry 8 bits 16 bits or more than that. There are mainly two types of buses
1.Address bus : 8051 Microcontroller consists of 16 bit address bus to assign address and identify memory positions. We can use adress bus to to carry 16 bit address from CPU to memory.
2. Data bus : We use 8 bits to indicate an ASCII character hence 8051 uses 8 bit data bus. It is used to carry a data. On width of data bus processing power of controller or processor depends.
Oscillator: Microcontroller 8051 consists of an on-chip oscillator which gives time source for CPU (Central Processing Unit). Generally we use crystal oscillator for stable oscillation, also we can connect external oscillator to 8051.
Interrupts : An interrupt is nothing but a signal to the processor send by external hardware or software which indicates an event that needs immediate service. The job of interrupt is to alert the controller regarding a high-priority event which require the interruption of the current routine code the controller is executing and service to some another time sensitive task. The controller acknowledges by suspending its current activities and saves the current states and executes a small program called as interrupt service routine, ISR) to deal with the time sensitive task. The interruption is not permanent, after completing ISR, the controller resumes execution from previous state. There are 5 interrupts in 8051, 2 hardware and 3 software. Some manufactures considers 'Reset' as an interrupt as well.
CPU: Central processing unit (CPU) is a brain of processor. The main components of a CPU are the arithmetic logic unit (ALU), which is used to perform arithmetic and logical operations, and the control unit (CU), which is used to extracts instructions from memory,decode it and executes them, also calls the ALU as per necessity.
We are mostly familiar with Central Processor Unit or CPU of computer. It manages as well as scrutinizes all processes that are carried out in the Computer. CPU executes the program written in (ROM) and do the projected duty.
Memory: Micro-controller i.e CPU needs the program's to do a specific tasks which is a set of commands. We have to store these programs on storage space i.e. memory . The memory which is used to store the program of Microcontroller is called as Program memory or generally we call it as a code memory. In most common language we call it "Read Only Memory" or ROM. Micro-controller also needs a short term memory space to perform operation on data stored in ROM . The storage space which is used for temporary data storage is called as Random Access Memory or RAM . 8051consist of program memory 4K byte and 128 bytes of a data RAM .
Bus: Bus is nothing but group of connecting wires which are used for the transfer Data. These buses are consist of 8, 16 or even more than that wires generally . Hence, a bus can carry 8 bits 16 bits or more than that. There are mainly two types of buses
1.Address bus : 8051 Microcontroller consists of 16 bit address bus to assign address and identify memory positions. We can use adress bus to to carry 16 bit address from CPU to memory.
2. Data bus : We use 8 bits to indicate an ASCII character hence 8051 uses 8 bit data bus. It is used to carry a data. On width of data bus processing power of controller or processor depends.
Oscillator: Microcontroller 8051 consists of an on-chip oscillator which gives time source for CPU (Central Processing Unit). Generally we use crystal oscillator for stable oscillation, also we can connect external oscillator to 8051.
Interrupts : An interrupt is nothing but a signal to the processor send by external hardware or software which indicates an event that needs immediate service. The job of interrupt is to alert the controller regarding a high-priority event which require the interruption of the current routine code the controller is executing and service to some another time sensitive task. The controller acknowledges by suspending its current activities and saves the current states and executes a small program called as interrupt service routine, ISR) to deal with the time sensitive task. The interruption is not permanent, after completing ISR, the controller resumes execution from previous state. There are 5 interrupts in 8051, 2 hardware and 3 software. Some manufactures considers 'Reset' as an interrupt as well.




Comments
Post a Comment